Unleash the Magic of Semrush: Supercharge Your SEO!
When it comes to optimizing your SEO campaigns, Semrush is a powerful tool that can truly work wonders. This all-in-one SEO platform is a game-changer for digital marketers, providing a comprehensive suite of features to help you boost your online presence and drive more traffic to your website.
One of the key benefits of using Semrush is its ability to conduct in-depth keyword research. By identifying the most relevant keywords for your industry and target audience, you can optimize your content and improve your search engine rankings. Semrush’s keyword research tool provides valuable insights into search volume, competition, and trends, allowing you to pinpoint the most effective keywords to target.
In addition to keyword research, Semrush offers a range of other features to help you supercharge your SEO efforts. The site audit tool, for example, scans your website for technical issues that could be affecting your search engine performance. By addressing these issues, you can improve your site’s overall health and ensure that it is easily crawlable by search engines.
Semrush also provides a backlink analysis tool, allowing you to monitor your website’s backlink profile and identify opportunities for link building. Backlinks are a critical factor in SEO, as they signal to search engines that your website is reputable and authoritative. By building high-quality backlinks from relevant websites, you can improve your search engine rankings and drive more organic traffic to your site.

Image Source: i0.wp.com
Another key feature of Semrush is its competitor analysis tool, which allows you to track your competitors’ online performance and identify areas where you can gain a competitive advantage. By analyzing your competitors’ keywords, backlinks, and content strategies, you can develop a more effective SEO strategy for your own website and stay ahead of the curve in your industry.
In addition to these core features, Semrush also offers a range of advanced tools to help you optimize your SEO campaigns. The on-page SEO checker, for example, analyzes your web pages and provides recommendations for improving your on-page optimization. This includes optimizing meta tags, headings, and content to ensure that your pages are fully optimized for search engines.
Semrush also offers a content marketing platform, which allows you to plan, create, and optimize your content for SEO. By identifying relevant topics and keywords, you can create content that resonates with your target audience and drives more traffic to your website. The content marketing platform also provides analytics to help you track the performance of your content and make informed decisions about future content strategy.
Overall, Semrush is a comprehensive tool that can help you unlock the full Potential of your SEO campaigns. By leveraging its powerful features and insights, you can supercharge your online presence, drive more traffic to your website, and outperform your competitors in the digital landscape. So why wait? Unleash the magic of Semrush today and take your SEO to the next level!
Transform Your Online Presence with Semrush Mastery!
Are you ready to take your online presence to the next level? With the power of Semrush at your fingertips, you can transform your SEO campaigns and unlock endless possibilities for success. Whether you’re a seasoned digital marketer or just starting out, mastering Semrush is the key to driving traffic, increasing conversions, and growing your business online.

Image Source: semrush.com
Semrush is a powerful all-in-one tool that offers a wide range of features to help you optimize your website for search engines. From keyword research to competitor analysis, backlink audits to site audits, Semrush has everything you need to stay ahead of the game in the ever-evolving world of SEO.
One of the first steps to mastering Semrush is familiarizing yourself with its user-friendly interface. The dashboard is organized in a way that makes it easy to navigate and find the information you need quickly. From the main dashboard, you can access all of Semrush’s features, including keyword research, site audits, and backlink analysis.
Keyword research is a crucial aspect of any successful SEO campaign, and Semrush makes it easy to find the best keywords for your website. By entering a seed keyword into the keyword research tool, Semrush will generate a list of related keywords along with important metrics like search volume, keyword difficulty, and CPC. This information is invaluable for determining which keywords to target in your content and optimizing your website for search engines.
Competitor analysis is another powerful feature of Semrush that can help you stay one step ahead of your competition. By entering your competitors’ websites into the tool, you can see valuable insights like their top-performing keywords, backlink profile, and traffic sources. This information can be used to identify gaps in your own SEO strategy and capitalize on opportunities to outrank your competitors in the search results.
Backlink audits are essential for monitoring the health of your website’s backlink profile and identifying any toxic links that could be harming your SEO efforts. Semrush’s backlink audit tool analyzes your website’s backlink profile and provides a list of Potentially harmful links that you can disavow to improve your website’s search engine rankings.

Image Source: backlinko.com
Site audits are another important aspect of SEO that Semrush excels at. By running a site audit, Semrush will analyze your website for technical SEO issues like broken links, missing meta tags, and duplicate content. This information can help you identify and fix any issues that could be holding your website back from ranking higher in the search results.
In addition to these core features, Semrush offers a wide range of additional tools and reports to help you optimize your SEO campaigns. From position tracking to on-page SEO recommendations, content analysis to social media monitoring, Semrush has everything you need to take your online presence to the next level.
With Semrush mastery, the sky’s the limit when it comes to optimizing your SEO campaigns and transforming your online presence. By leveraging the power of Semrush’s advanced features and tools, you can drive more traffic to your website, increase conversions, and ultimately grow your business online. So what are you waiting for? Unlock the power of Semrush today and take your online presence to new heights!
How to Use Semrush for SEO Campaigns
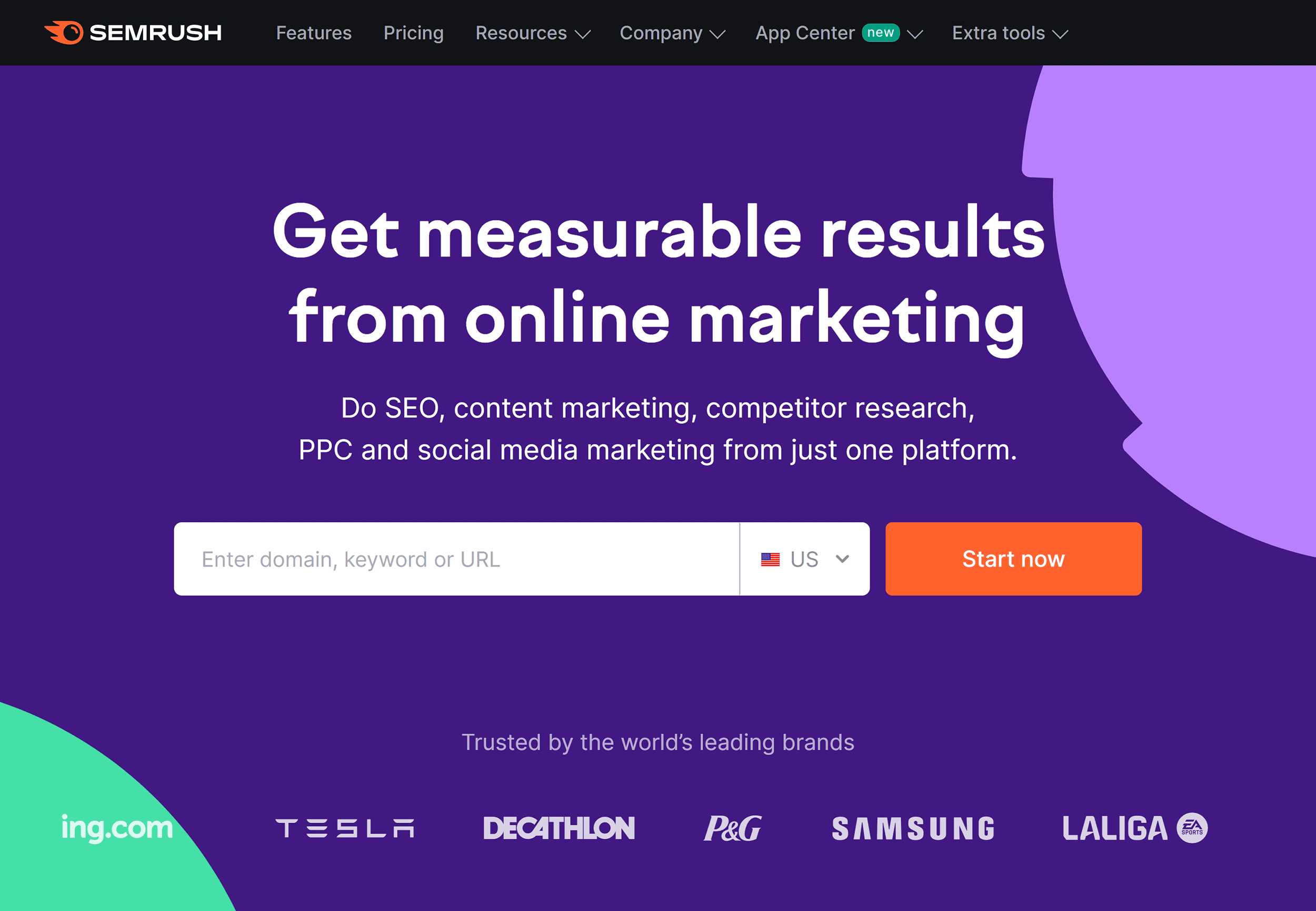
Image Source: backlinko.com

Image Source: semrush.com

Image Source: leannewong.co

Image Source: backlinko.com

Image Source: semrush.com

Image Source: ytimg.com
