Avocados, also known as nature’s Butter, are a versaTile and delicious Fruit that is packed with nutrients. They are not only tasty but also incredibly good for your health. In this article, we will explore the top 10 health benefits of eating avocados.
1. Rich in Nutrients
Avocados are a nutrient-dense fruit, containing a wide variety of vitamins and minerals. They are particularly high in vitamins C, E, K, and B-6, as well as riboflavin, niacin, folate, pantothenic acid, magnesium, and Potassium. In fact, avocados are one of the most nutrient-rich fruits you can eat.
2. Heart-Healthy Fats
Avocados are rich in monounsaturated fats, which are heart-healthy fats that can help reduce bad cholesterol levels and lower your risk of heart disease. These fats also help your body absorb other nutrients, making avocados a great addition to any meal.
3. Aids in Weight Management
Despite their high fat content, avocados can actually help with weight management. The monounsaturated fats in avocados can help you feel full and satisfied, reducing your overall calorie intake. Additionally, the fiber in avocados can help regulate your digestion and keep you feeling full for longer.

Image Source: intuit.com
4. Improves Digestion
Avocados are an excellent source of fiber, which is essential for healthy digestion. Fiber helps regulate bowel movements, prevent constipation, and maintain a healthy gut microbiome. By including avocados in your diet, you can promote better digestion and overall gut health.
5. Boosts Brain Health
Avocados are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for brain health. These fats can help improve cognitive function, enhance memory, and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. By eating avocados regularly, you can support your brain health and overall cognitive function.
6. Supports Eye Health
Avocados are high in antioxidants such as lutein and zeaxanthin, which are important for eye health. These compounds can help protect your eyes from age-related macular degeneration and cataracts, and promote overall eye health. Including avocados in your diet can help protect your vision as you age.
7. Reduces Inflammation
Avocados contain anti-inflammatory compounds that can help reduce inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is linked to a variety of health problems, including heart disease, arthritis, and cancer. By including avocados in your diet, you can help reduce inflammation and lower your risk of these diseases.
8. Supports Skin Health
The vitamins and antioxidants in avocados can also benefit your skin. Vitamin E, in particular, is known for its ability to promote skin health and reduce signs of aging. By eating avocados, you can nourish your skin from the inside out and achieve a healthy, glowing complexion.

Image Source: website-files.com
9. Regulates Blood Sugar Levels
Avocados have a low glycemic index, which means they have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. This makes them a great option for people with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar levels. The healthy fats and fiber in avocados can also help stabilize blood sugar levels and prevent spikes and crashes.
10. Boosts Immune Function
Lastly, avocados are packed with vitamins and antioxidants that can help boost your immune system. Vitamin C, in particular, is known for its immune-boosting properties and can help protect your body against illnesses and infections. By including avocados in your diet, you can support your immune function and stay healthy year-round.
In conclusion, avocados are not only delicious but also incredibly good for your health. From heart-healthy fats to immune-boosting vitamins, avocados offer a wide range of health benefits that can support your overall well-being. So next time you’re looking for a nutritious and tasty snack, reach for an avocado and enjoy all the amazing benefits it has to offer.
How to Manage Your Taxes as a Freelance Web Designer
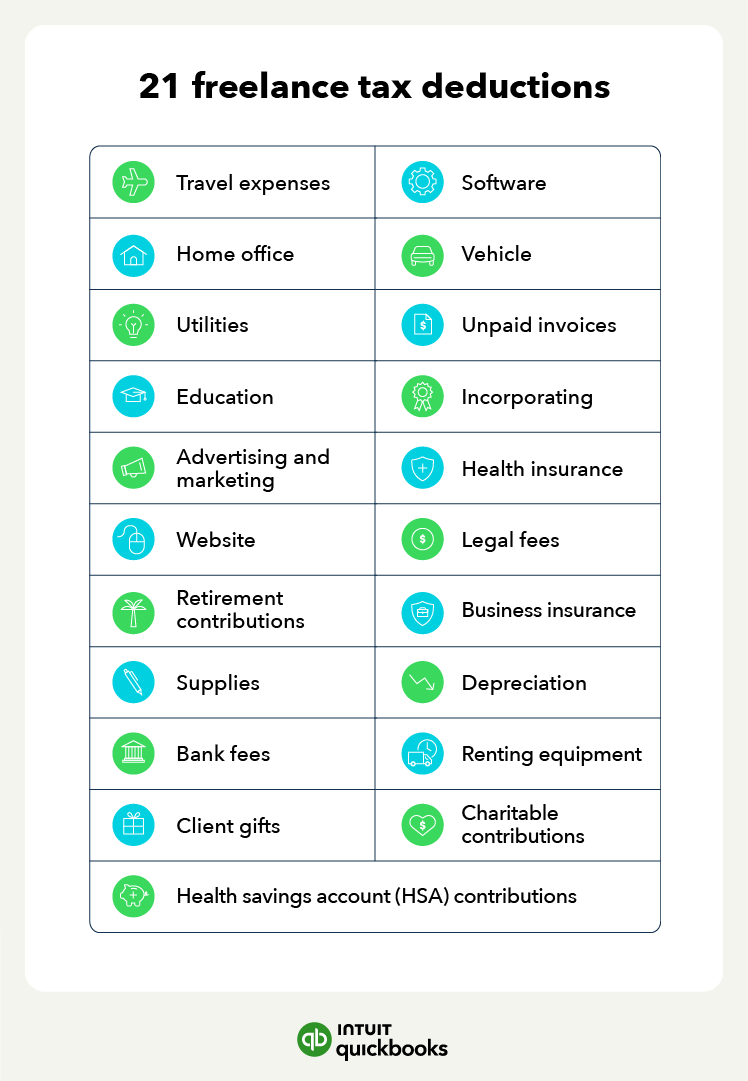
Image Source: intuit.com

Image Source: ytimg.com

Image Source: ytimg.com

Image Source: ytimg.com

Image Source: medium.com
